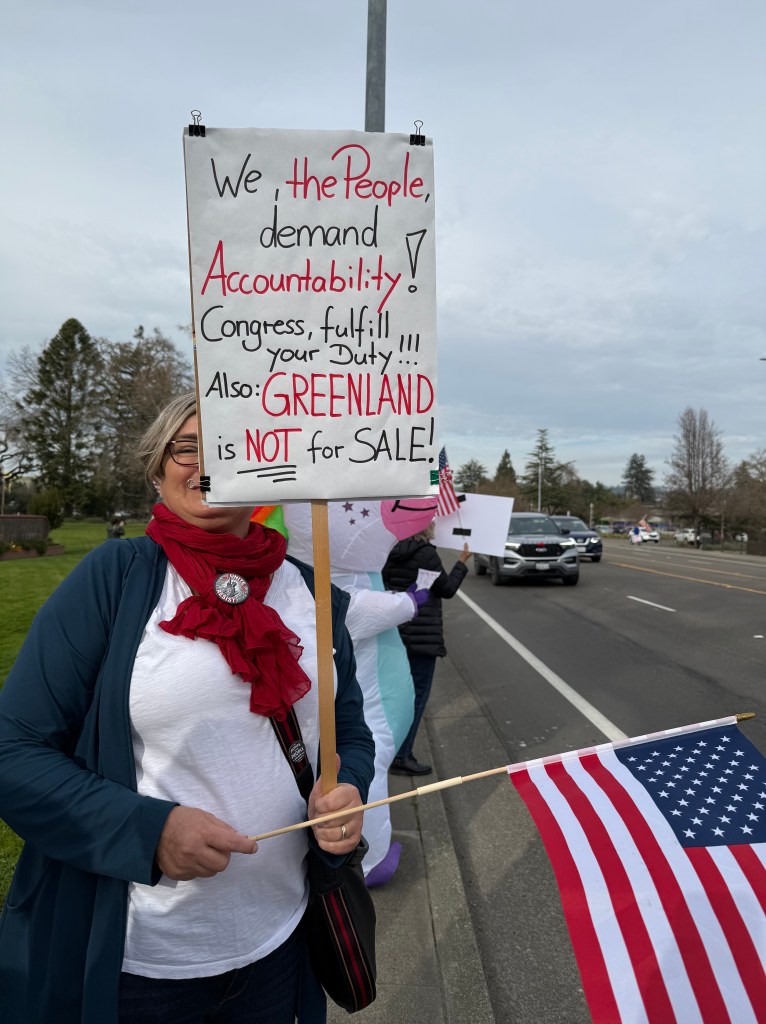
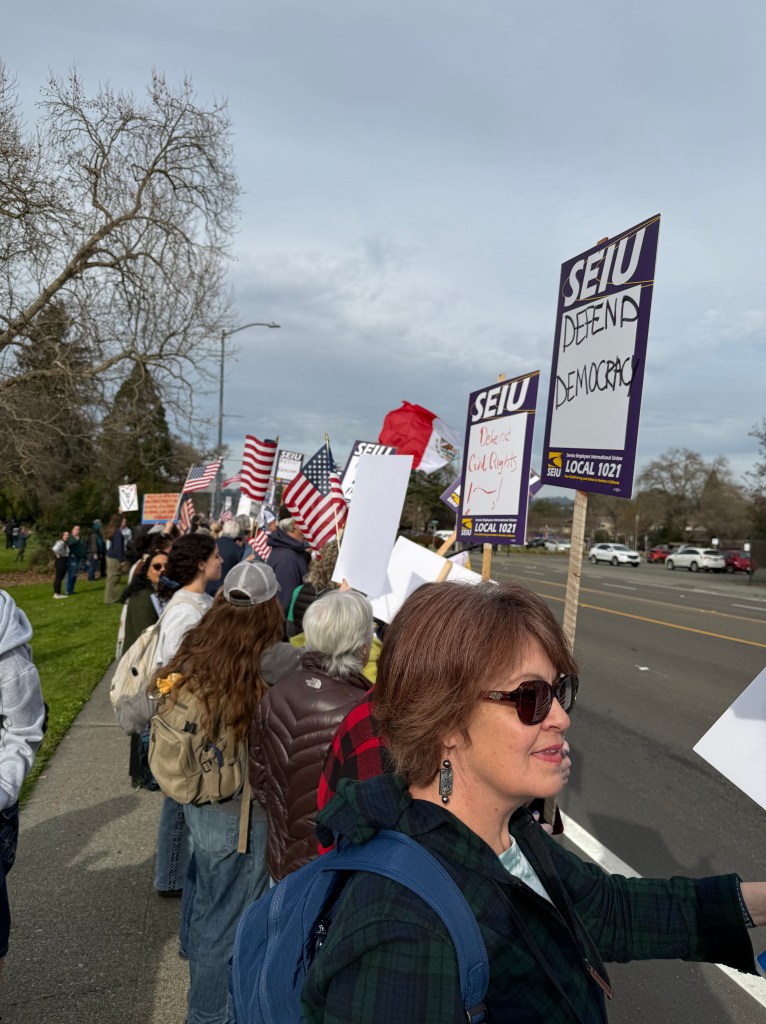
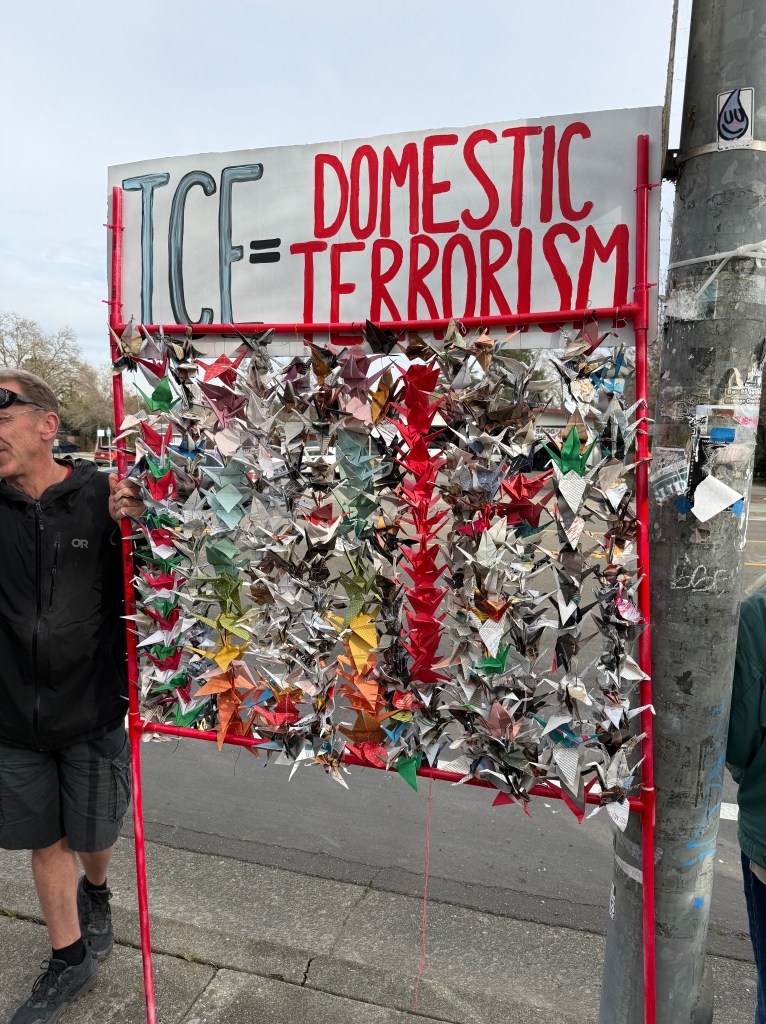
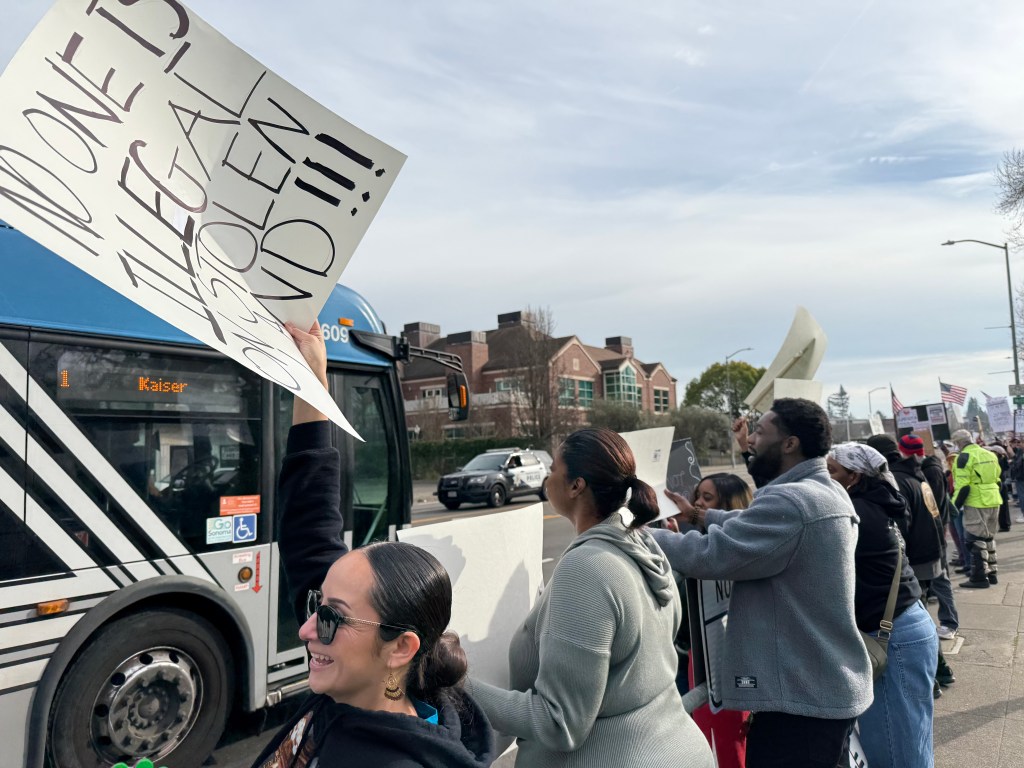
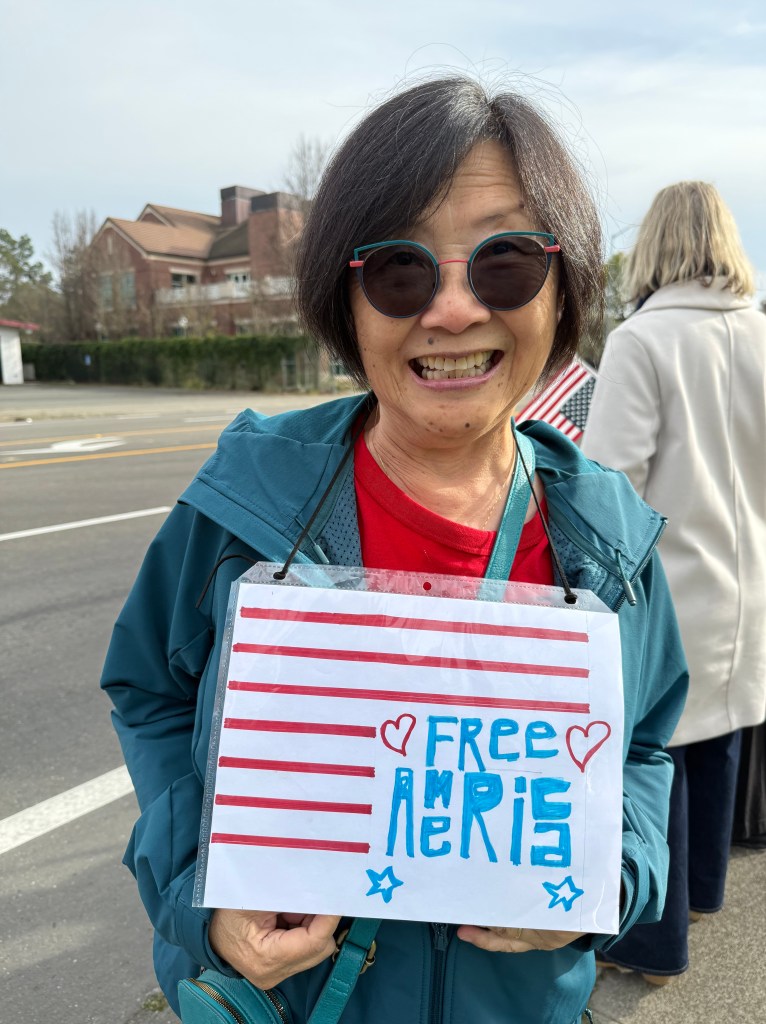
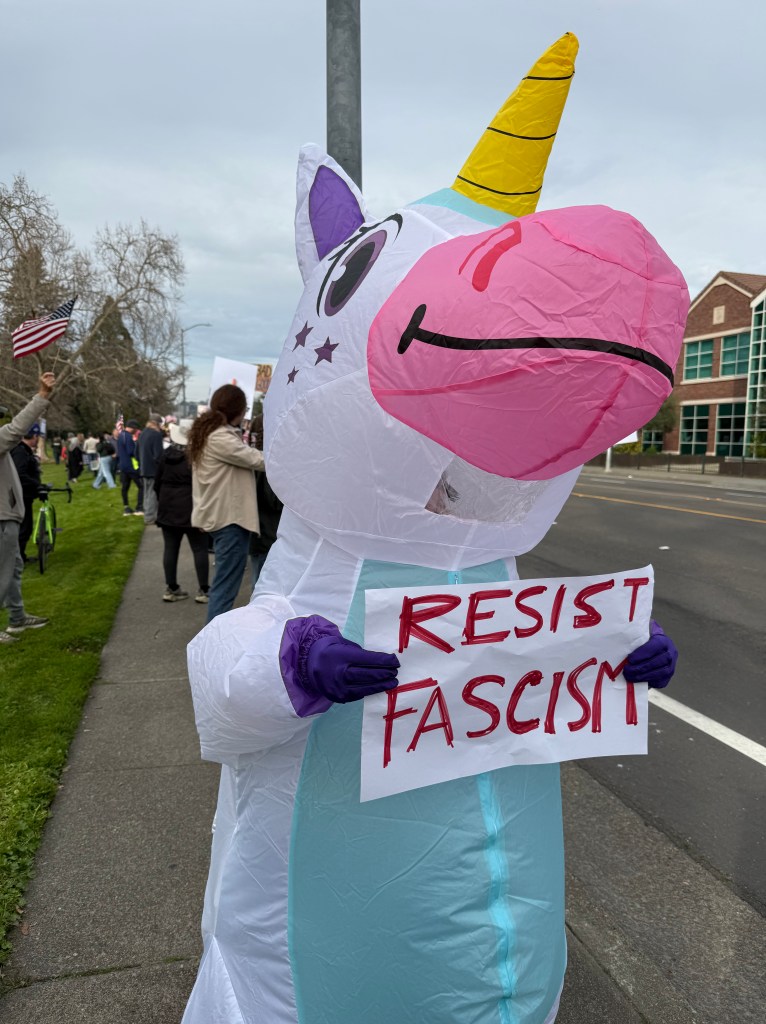
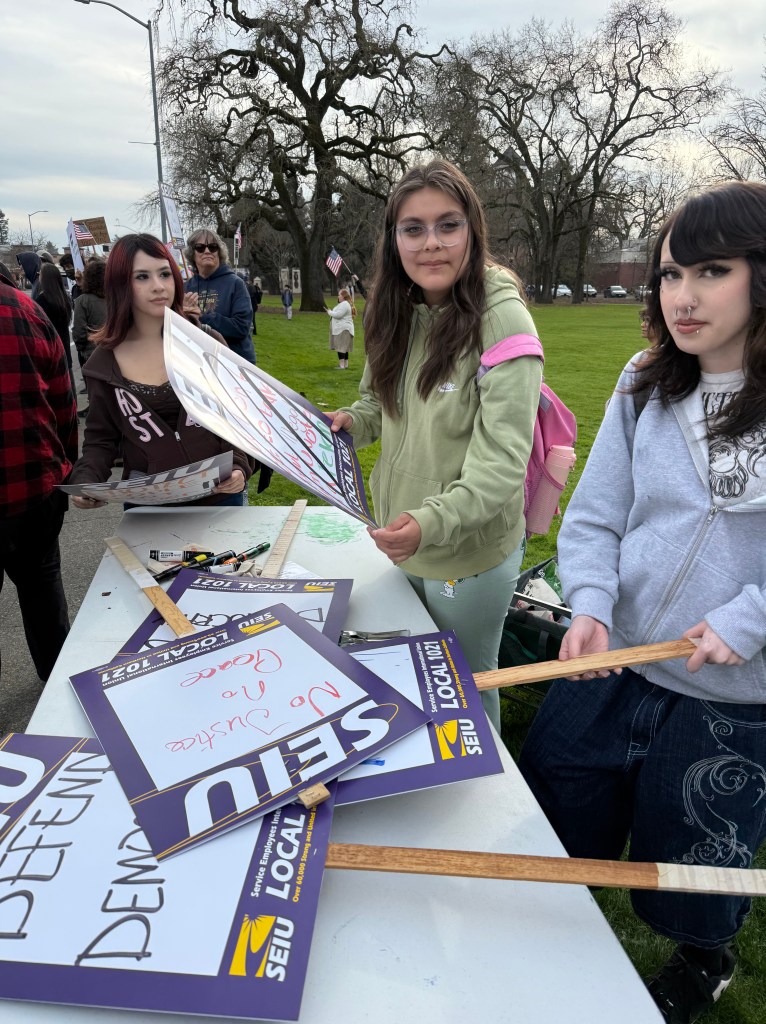
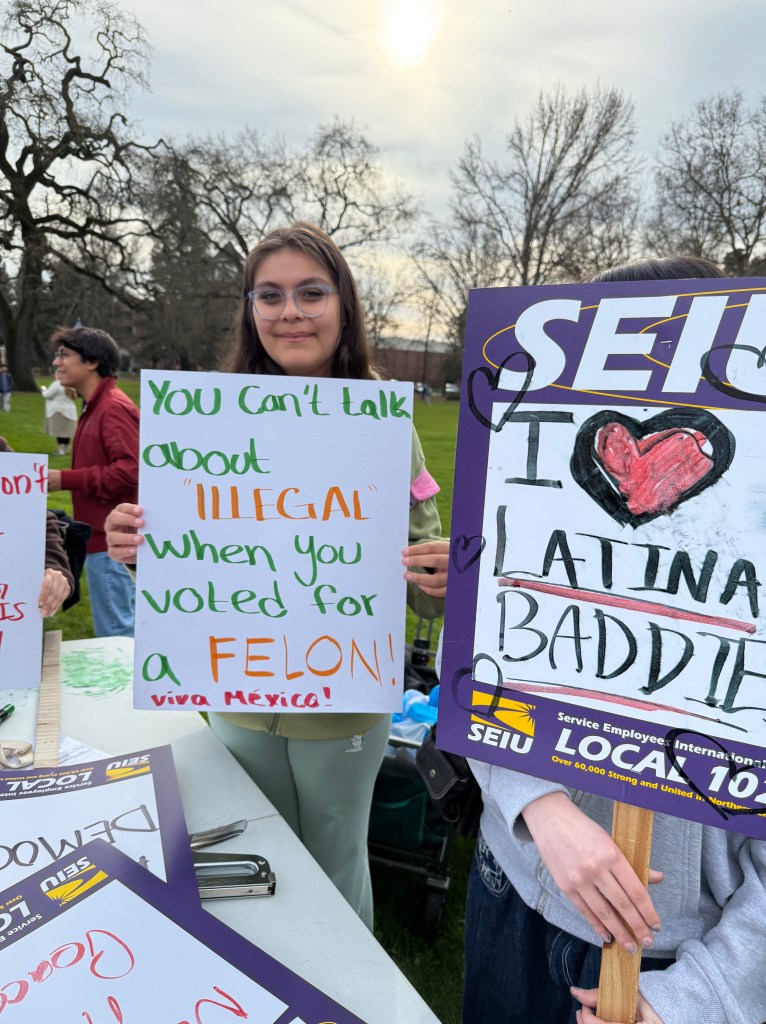
With Santa Rosa Women’s March and SEIU Local 2021
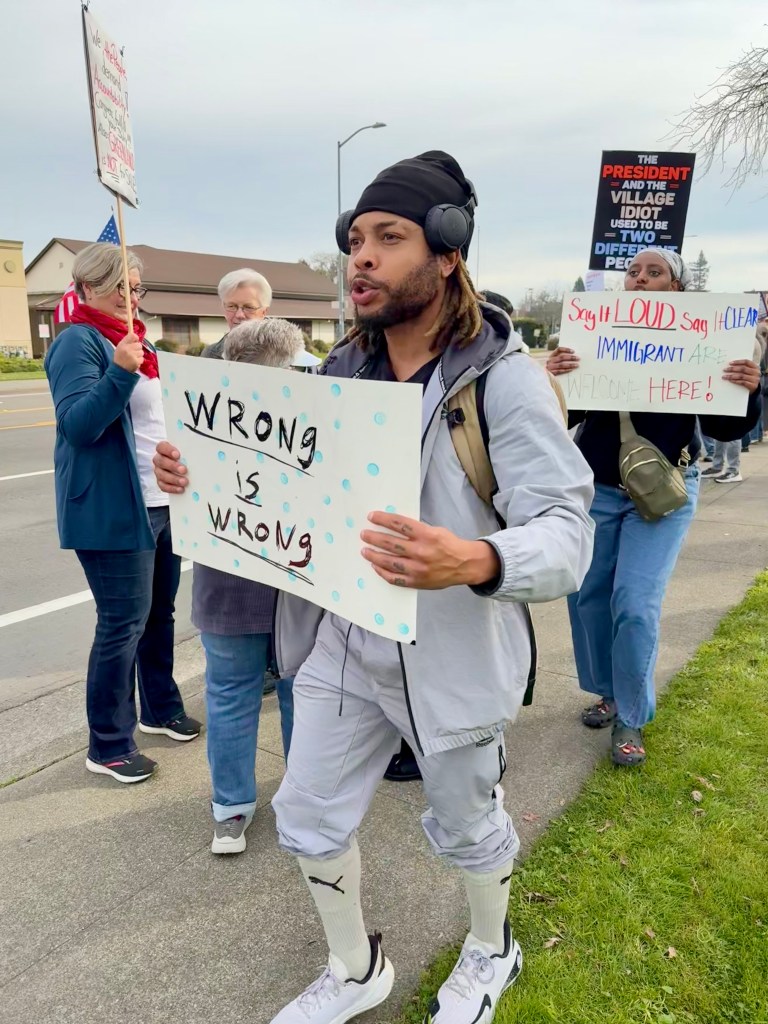
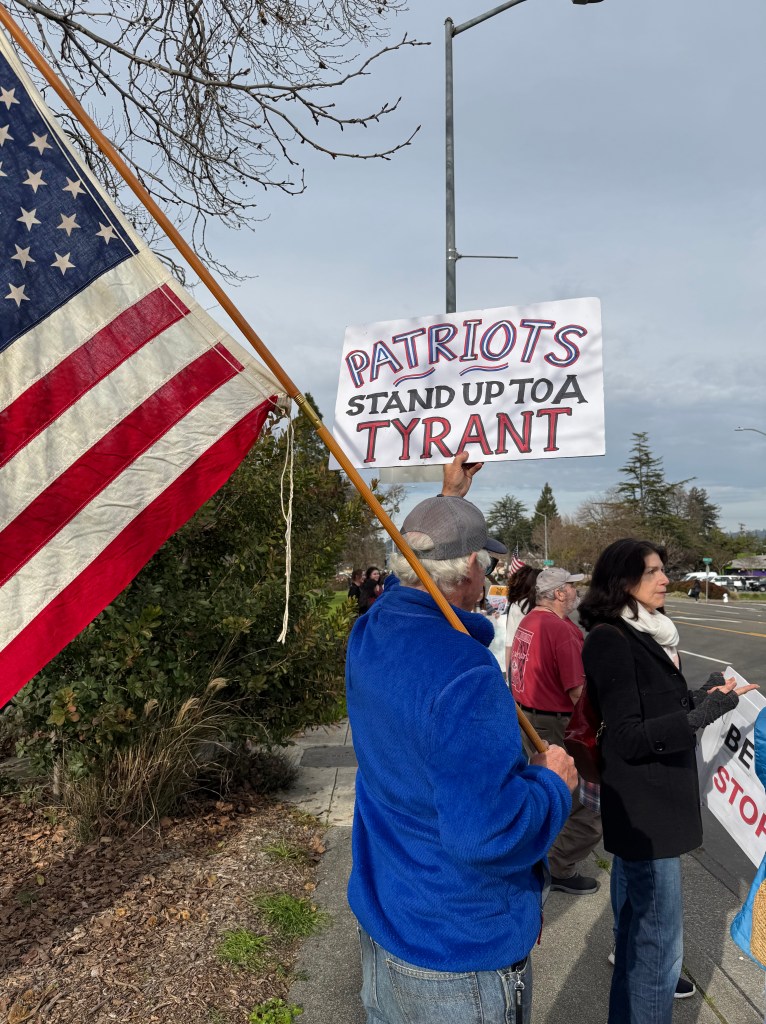
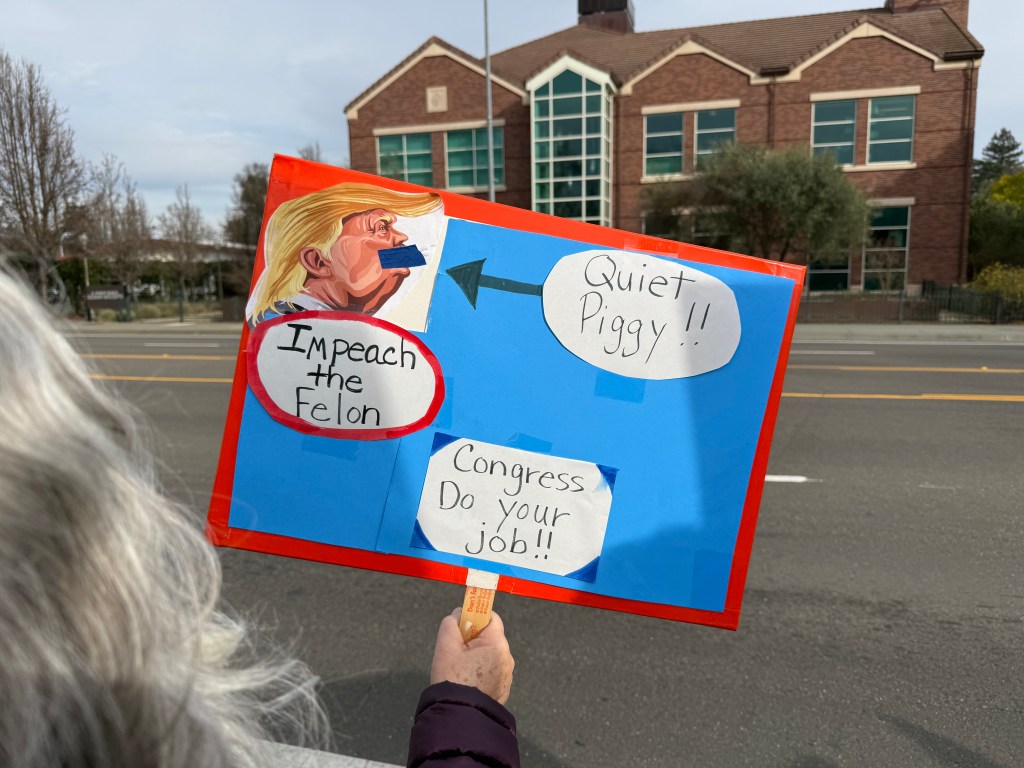
Folks Get Creative With Their Signs





















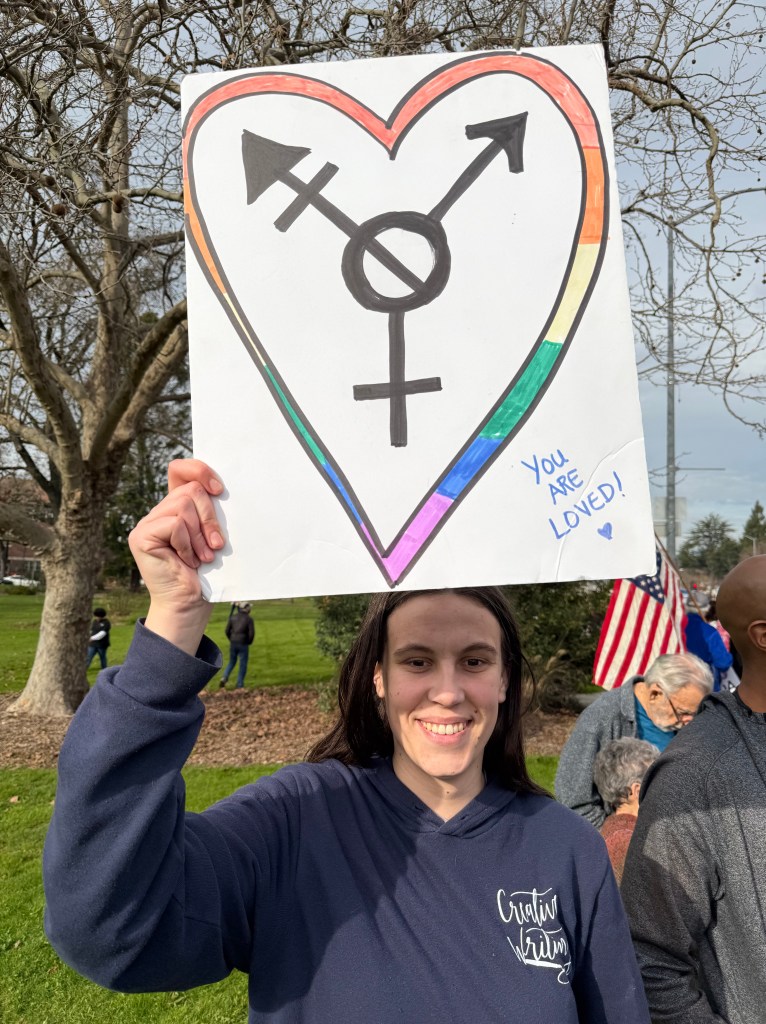






















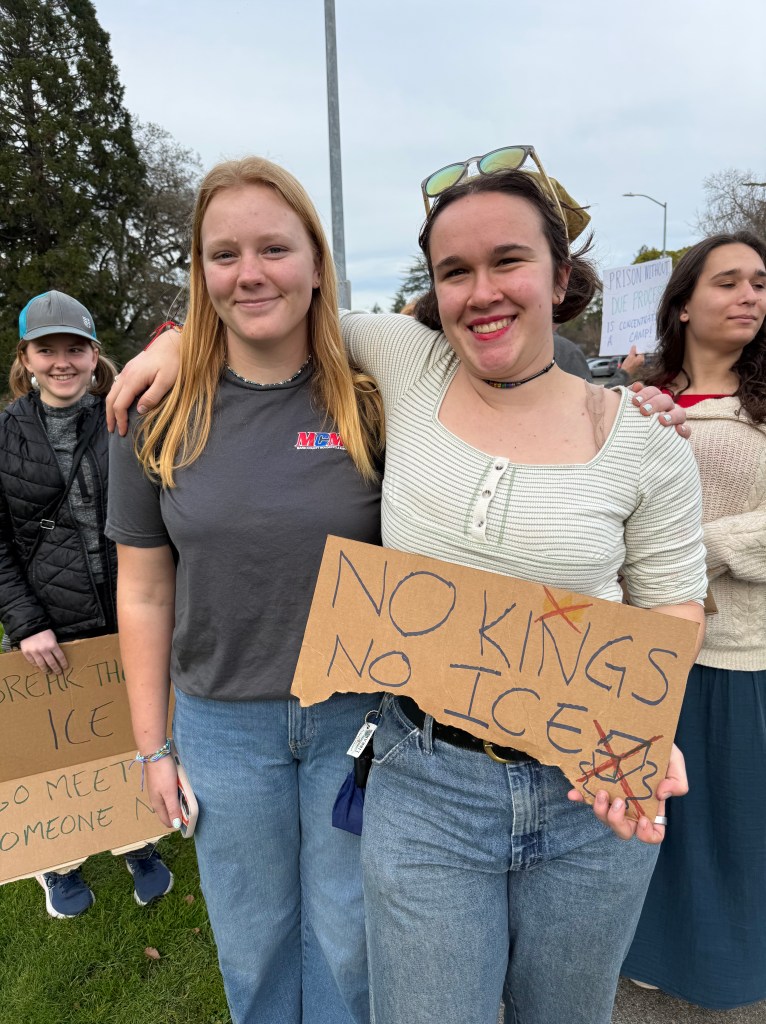
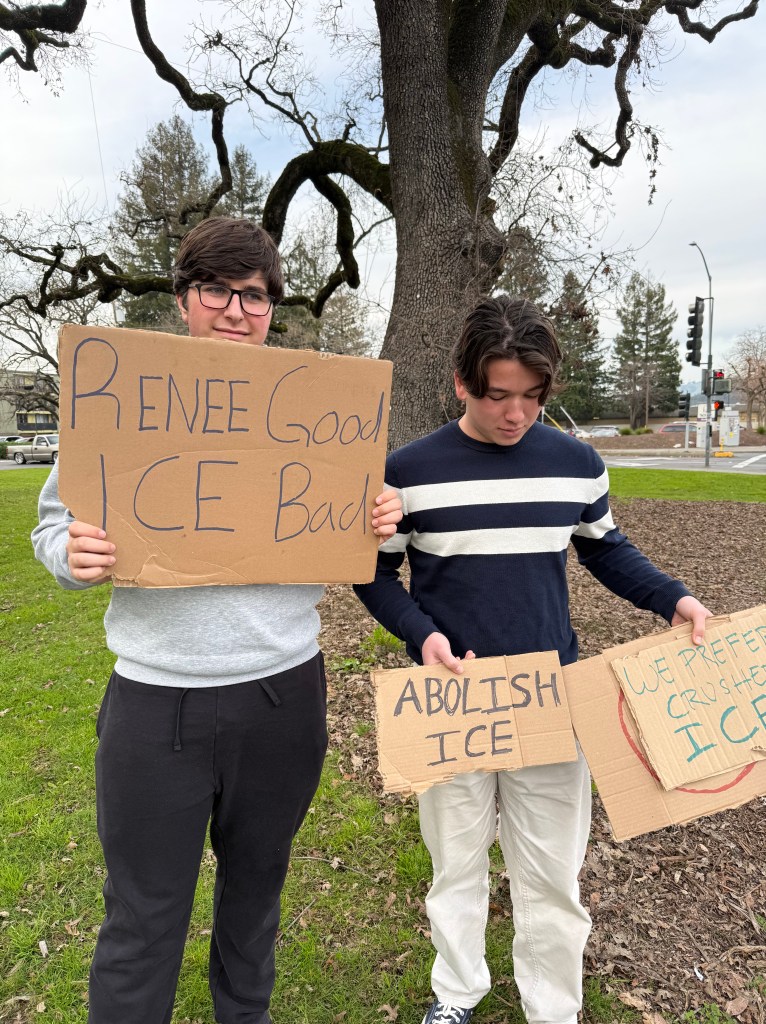
IBEW Canada Statement Mourning the Loss of Amber Czech and Condemning Violence in the Workplace
Toronto, ON – November 17, 2025
Today, International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW) Canada International Vice President Russ Shewchuk issued the following statement:
“IBEW Canada mourns the loss of 20-year-old welder Amber Czech, who was brutally attacked and killed at her workplace in Minnesota. We extend our deepest condolences to Amber’s family, friends, fellow workers and her community.
“Although Amber was not a member of the IBEW or affiliated Building Trades Unions (NABTU/CBTU), what happened to her should never happen to anyone—anywhere. And while this tragedy occurred in the U.S., the loss is deeply felt across our union community in Canada. It’s a stark reminder of the work we must keep doing to ensure such senseless acts never happen again.
“Violence has no place on our job sites, in our offices, or in our union. We owe it to Amber, and to every worker who has been harmed or threatened, to build safe, respectful, and inclusive working environments, free of violence and cruelty.
“IBEW Canada stands with all who advocate for ending gender-based violence, and all violence in the workplace. We commit to ongoing training, conversation and action that promote equity and dignity for all workers.”
###
Media Contact: Shaina Hardie, shaina_hardie@ibew.org
The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW) represents approximately 70,000 members in Canada and 873,000 members and retirees in North America who work in a wide variety of fields, including construction, utilities, manufacturing, telecommunications, broadcasting, railroads and government. For more information, visit IBEWcanada.ca or IBEW.org
It’s time for our US labor unions to condemn workplace violence and do something about it.
Indictment means possible life term for man accused of killing co-worker in Wright County workshop
One major labor organization noted that “violence like this rarely comes out of nowhere. It often follows a buildup that women in the trades know by heart.”
The Minnesota Star Tribune
DECEMBER 8, 2025 AT 10:41AM

The man accused of killing a co-worker last month with a hammer in a Wright County workshop now faces a charge of first-degree murder and a potential life prison sentence in a slaying that drew outcry by advocacy groups for women in the trades.
A grand jury heard the case last week against David Bruce DeLong, 40, of Watkins, Minn., and indicted him on a charge of first-degree premeditated murder in connection with the attack in Cokato that killed 20-year-old Amber Mary Czech of Hutchinson, Minn.
The bludgeoning occurred on Nov. 11 at Advanced Process Technologies, which makes equipment used in food processing.
County Attorney Brian Lutes said the first-degree count carries a mandatory sentence of life in prison without parole. DeLong also faces a second-degree murder charge.
DeLong remains jailed in lieu of $2 million bail ahead of a court appearance Monday. The Minnesota Star Tribune has reached out to his attorney for a response to the allegations.
An online fundraising campaign started to cover funeral expenses noted that “Amber was a hardworking welder who took great pride in her craft and dreamed of building a bright future through her work. Her witty personality, positive attitude, and beautiful smile touched everyone who knew her.”
Numerous labor organizations decried the workplace killing of Czech, including the International Association of Sheet Metal, Air, Rail and Transportation Workers (SMART), with 230,000 members in North America.
“While not a SMART member … this tragedy is reverberating across the trades community and far beyond,” read a statement from the organization. “So many tradeswomen and gender-diverse workers are carrying the weight of this news.”
SMART went on to point out that “violence like this rarely comes out of nowhere. It often follows a buildup that women in the trades know by heart: harassment shrugged off, bullying tolerated, intimidation minimized, warning signs dismissed, fear of backlash, comments ignored, jokes explained away, the stares of resentment, and behaviors everyone chooses not to see until they can no longer look away.”
The Laborers’ International Union of North America (LIUNA), which counts 500,000 workers across many industries among its ranks, said in a statement, “When a young tradeswoman’s future is so violently crushed, we must look to the criminal justice system to do its job — but as brothers and sisters in the construction trades we must also do much, much more. … We must not only condemn the violence that took Czech’s life but also the attitudes and behavior that normalize an atmosphere of fear for too many construction craftswomen.”
David Bruce DeLong (Wright County jail)
Around 6 a.m., a caller to 911 said Czech was bleeding heavily from a blow to the head, and there was a bloody sledgehammer on the floor nearby. Emergency medical responders arrived and declared her dead at the scene.
A sheriff’s deputy identified DeLong as the suspected attacker. DeLong said to a man at the business “something to the effect of, ‘I hit her with your hammer. She is by your toolbox. She is gone,’” the complaint read.
Sheriff’s deputies reviewed surveillance video inside the business and saw DeLong walk from his workstation to Czech’s, grab a sledgehammer and swing it. The victim was out of view of the camera.
DeLong’s swings indicated that he targeted her once while she was standing and four more times after she fell to the floor.
After his arrest, DeLong confessed to killing Czech. He said he didn’t like her and had been “planning to kill [her] for some time,” the complaint continued.
Say Her Name: Amber Czech
https://19thnews.org/2025/11/amber-czech-welder-murder-tradeswomen-demand-action/
Tradeswomen Organize for Job Safety
She was not the first. I wrote about the murder of another tradeswoman in 2017: https://mollymartin.blog/2024/06/27/a-sisters-murder-sparks-action/
The 6888th Battalion cleaned up the mail mess
My Mother and Audie Murphy Ch. 43
In October 1944, after her fiancé Gene was killed, Flo had trouble reaching her mother. The wartime mail system was broken.
This wasn’t just a personal problem—it was widespread. Soldiers on the battlefield were not receiving letters and packages from home. Mail, the lifeline of morale, was piling up undelivered. The men risking their lives for democracy weren’t hearing from their families, and the silence was taking a serious toll.
Flo had noticed the problem early. In letters and diary entries beginning in May 1944, shortly after arriving in Italy, she often mentioned that no mail had come. She didn’t complain—Flo wasn’t a complainer—but she noted it again and again. Others were more vocal. Across the war front, soldiers and Red Cross workers alike were frustrated and bitter. What began as a logistical issue had grown into a morale crisis.
The Army didn’t officially acknowledge the scale of the problem until 1945—by then, millions of letters and packages were sitting in European warehouses, unopened and unsorted.
Then came the 6888th.

The 6888th Central Postal Directory Battalion—known as the “Six Triple Eight”—was a groundbreaking, all-Black, multi-ethnic unit of the Women’s Army Corps (WAC), led by Major Charity Adams. It was the only Black WAC unit to serve overseas during the war.
Their mission: clear the massive backlog of undelivered mail under grueling conditions and extreme time pressure. They worked in unheated warehouses, with rats nesting among the mailbags, and under constant scrutiny from a military establishment rife with racism and sexism. But they got the job done—sorting and forwarding millions of pieces of mail in record time.
Their work restored something vital: connection. And morale.
The 6888th wouldn’t have existed without the efforts of civil rights leaders. In 1944, Mary McLeod Bethune lobbied First Lady Eleanor Roosevelt to support the deployment of Black women in meaningful overseas roles. Black newspapers across the country demanded that these women be given real responsibility and not sidelined. Eventually, the Army relented.
The women of the 6888th made their mark. Many would later say they were treated with more dignity by Europeans than they had ever experienced in the United States.
If you haven’t seen the Netflix movie The Six Triple Eight, it’s well worth your time.
Back in October 1944, the broken mail system meant heartbreak and silence for Flo. How long did it take for her disconsolate letter to reach her mother? Gerda telegrammed back on November 14—more than two weeks after Gene had died.

When did Flo receive Gene’s final letters? She saved the ones he wrote on October 24 and 27, but it seems likely she didn’t get them until after he was gone. He died on October 28, killed by a mortar shell. That same day, Flo wrote in her diary, “Mail from home today.” She didn’t mention anything from Gene.
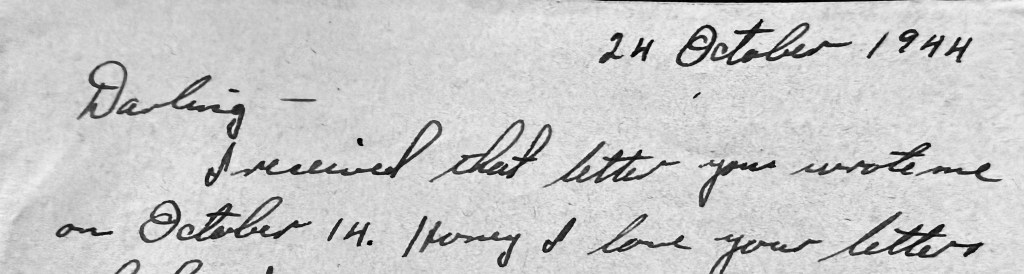
In his last letters, Gene wrote about his army buddies. He worried about his little sister wanting to marry. He dreamed of peace, and of a life with Flo in the Northwest:
“Back there where the country is rugged and beautiful. Where you can breathe fresh, free air; and fish and hunt to your heart’s content. You know honey, a place where we don’t have to sleep in the mud and cold, and where the shrapnel doesn’t buzz around your ears playing the Purple Heart Blues.”
Even in the chaos of war, he tried to stay lighthearted:
“I’m writing on my knees with a candle supplying the light. I hope you are able to read it. My spelling isn’t improving very much; but with the aid of a dictionary I may improve or at least make my writing legible.”
He hoped Flo had managed a trip to Paris, and that she’d seen her sister and brother-in-law stationed there. He looked forward to getting married:
“Honey I haven’t heard from home on the ring situation yet, but I expect to before long. When I do, I shall let you know right away. I’m hoping we can make it so by xmas, if not before.”
But his letters also reflected the danger he was in:
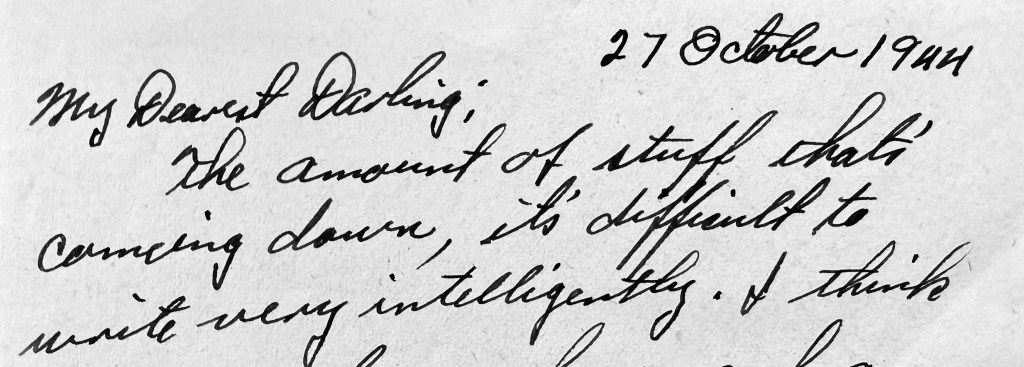
“It’s very difficult to write a letter on one’s knees, as you probably already know. Ducking shrapnel and trying to write just don’t mix. I do manage to wash and brush my teeth most every day.”
“It’s too ‘hot’ for you to be here. I’ve got some real stories to tell you when I see you next—if I’m not too exhausted. You don’t know how close you’ve been to—I hadn’t better tell you.”
Gene’s voice comes through with vivid clarity, even across 80 years and a broken mail system.

That words eventually reached soldiers in the field and their families back home is thanks, in part, to the quiet heroism of the 6888th—who made sure love letters, grief, and hope could still find their way through a war.
Ch. 44: https://mollymartin.blog/2025/08/02/born-in-oregon-buried-in-france/
Neighbors Getting Ready for the Big Demonstration Saturday
The Black Freedom Movement and Tradeswomen History
I want to take us back in time and imagine a world, a culture, in which job categories were firmly divided between MEN and WOMEN. Women were restricted to pink collar jobs that paid too little to raise a family on or even to live without a man’s support. Even doing the same jobs, women were legally paid less than men. Married women were not allowed to work outside the home. Single women who found jobs as teachers or secretaries were fired as soon as they married. Black people were only allowed to work as laborers or house cleaners.
This was the world we fought to change.
Tradeswomen who have jobs today must thank Black workers who began the fight for jobs and justice.
The Black Freedom Movement has advocated for workplace equity since the end of the Civil War.
The movement gained power during and after WWII. A. Philip Randolph headed the sleeping car porters union, the leading Black trade union in the US. In 1940 he threatened to march on Washington with ten thousand demonstrators if the government did not act to end job discrimination in federal war contracts. FDR capitulated and signed executive order 8802, the first presidential order to benefit Blacks since reconstruction. It outlawed discrimination by companies and unions engaged in war work on government contracts. This executive order marked the start of affirmative action.
The fight to desegregate the workforce continued.
In the early 1960s in the San Francisco Bay Area, protesters organized successful picket campaigns against businesses that refused to hire Blacks, including the Palace hotel, car dealerships and Mel’s Drive-In. Many of the protesters were white students at UC Berkeley.
In August 1963, the march on Washington brought 200,000 people to the capitol to protest racial discrimination and show support for civil rights legislation. The civil rights act of 1964, signed into law by President Johnson, is the legal structure that women and POC have used to put nondiscrimination into practice.
But change did not come quickly or easily.
Black workers at a tire plant in Natchez Mississippi were organizing to desegregate jobs. The CIO, Congress of Industrial Organizations, supported them in this fight. In 1967, three years after the civil rights act became law, a Black man, Wharlest Jackson, who had won a promotion to a previously “white” job in the tire plant, was murdered by the KKK. They blew up his truck as he was driving home from work. No one was ever arrested or prosecuted for this crime.
Wharlest Jackson was the father of five. His wife, Exerlina, was among those arrested for peacefully insisting on equal treatment during a boycott of the town of Natchez’s white businesses. She was sent to Parchman penitentiary.
Jackson was just one of many who died for our right to be treated equally at work.
Tradeswomen are part of the feminist, civil rights and union movements. We continue to seek allies because we are few.
Discrimination has not ended, but, because of decades of organizing, our work lives have improved. We owe much to the Black workers who sought equity in employment for decades before us.
Photo: the Zinn Education Project